INSULATED GLASS UNITS
Insulated Glass Units (IGUs) consist of two or more glass panes that are spaced apart and sealed with a sealant to create a unified unit. Commonly known as double glazing, IGUs are engineered to minimize heat loss and solar heat gain entering buildings, while also reducing visible light transmittance. Consequently, they enhance thermal performance and decrease energy expenses. Moreover, IGUs can be tailored to fulfill various requirements, including sound control, seismic resilience, bullet resistance, hurricane and blast resistance, impact resistance, and compliance with state energy codes. By integrating laminated glass products, tinted glass, Low-E coatings, reflective coatings, silk-screened patterns, and other elements, a broad spectrum of insulating glass configurations can be produced to cater to diverse aesthetic and performance demands.
Components
Glass lites:
An Insulated Glass Unit (IGU) comprises at least two panes, or lites, of glass. While monolithic glass is commonly used in IGUs, other types of coated and laminated glasses may be employed based on the specific application to enhance unit performance.
Desiccant:
The frame, also known as the spacer bar, is utilized to separate the two glass lites within an IGU. Typically crafted from aluminum and filled with desiccant, it plays several crucial roles. These include maintaining unit integrity, providing thickness and mechanical resilience, and ensuring optimal unit performance.
Filling:
There are three primary types of IGUs categorized by the gas filling between the glass lites. The first type involves no filling and contains dry air. The second type incorporates inert gas filling, such as argon, krypton, or xenon, to enhance insulation properties.
Sealant:
Sealants play a vital role in IGU manufacturing due to their efficiency, ease of handling, environmental friendliness, and safety. They are esteemed for their adhesion, elasticity, and durability. Additionally, they exhibit favorable curing characteristics, including low moisture vapor transmission rates.


Benefits:

Reduced Infiltration
In colder climates, the objective is to minimize the infiltration of cold air, maintain internal heating, and decrease heating costs. IGUs contribute significantly to achieving these goals.
Reduced Condensation
Condensation can lead to water damage on window sills and frames, as well as seepage into adjacent walls and areas. Window surfaces, being colder than other building surfaces, are particularly prone to condensation buildup. IGUs mitigate the likelihood of condensation by providing a thermal barrier between the interior and exterior environments.
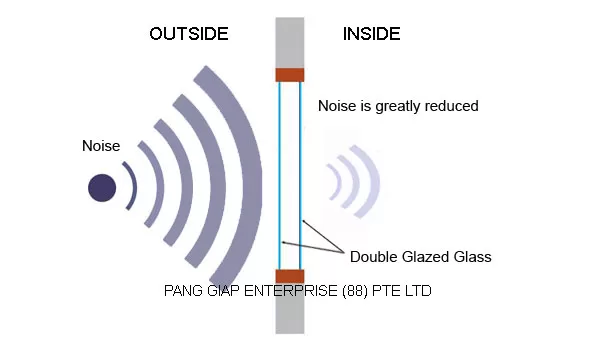
Acoustic Insulation
Monolithic glass tends to resonate when exposed to high-frequency sound due to its inability to withstand such frequencies. IGUs effectively reduce sound transmission by trapping air within the unit, preventing resonance from passing through. For example, buildings situated near airports, railway stations, and busy roads often utilize IGUs to minimize external noise intrusion.
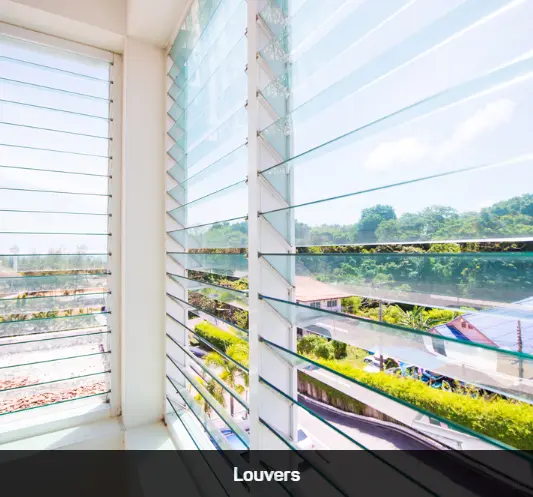
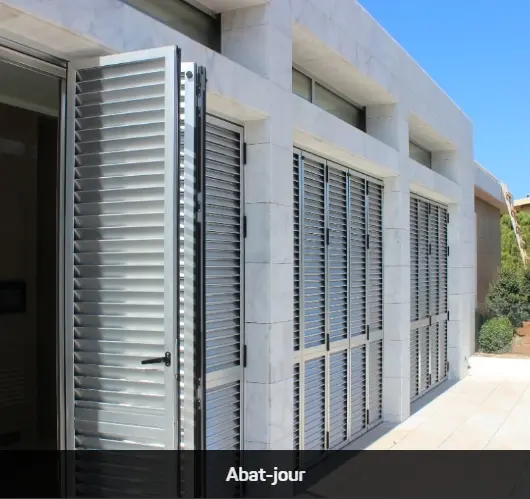
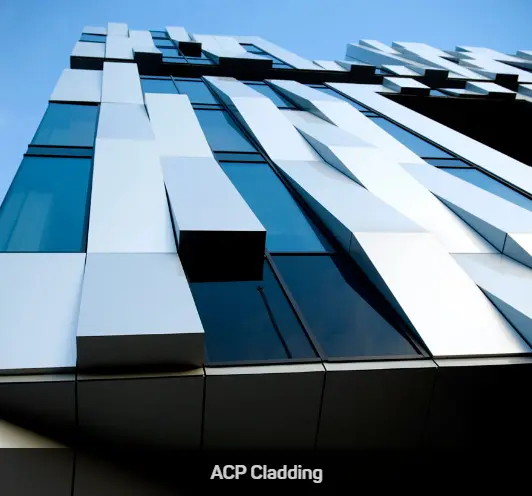
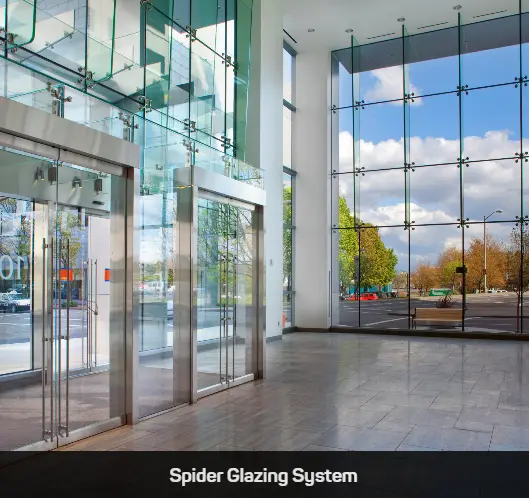
Explore Our Products

With over 55 years of dedication, our business stands at the forefront of the Aluminum and Glass industry. From humble beginnings in the 1960s to four cutting-edge facilities spanning thousands of square feet, our commitment to precision and innovation remains unwavering. Backed by seasoned engineering and meticulous manufacturing processes, we deliver excellence with every product, embodying a legacy of reliability and expertise.














